You are here: Language Elements and Expressions > String Expressions
Any text to be written to a file or displayed on the screen is created with a string expression. String expressions are created from a combination of the following:
A string expression must begin with a concatenation operator ($) or with a string constant in quotes (i.e., "..."). The concatenation operator combines components together, and must be between all components of a string expression. For example, if Attr1 is 7.83, then the expression "STRING1"$ ATTR1 $ "STRING2" evaluates to "String17.83String2."
To output the name of a location, entity, or resource, use the appropriate function inside a string expression: LOC() for locations, ENT() for entities, and RES() for resources. For example, the following logic checks the first ten locations in a model and displays the name of any location that is completely full.
Display name of full location
Var1 = 1
While Var1 <= 10 Do
Begin
If FreeCap(Loc(Var1)) = 0 Then
DISPLAY Loc(Var1) $ "is full."
INC Var1
End
String expressions are valid only as part of the following statements and functions: DISPLAY, PAUSE, PROMPT, STOP, WRITE, WRITELINE, TRACE, XSUB(), and XWRITE.
String expressions
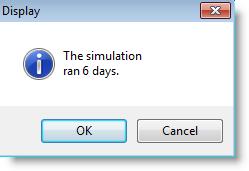
If a model had been running for six days, the statement
DISPLAY "The simulation ran \n" $ CLOCK(DAY) $ "days."
would display the following dialog box.
